近期,本课题组张敏老师和刘德行同学、刘子一同学分别以通讯作者和共同第一作者在材料科学和工程技术领域顶级期刊 Advanced Materials (Nature-index期刊,影响因子29.4)上发表题为“Hydrogen-Bonding Integrated Low-Dimensional Flexible Electronics beyond the Limitations of Van Der Waals Contacts”的文章,从理论计算和表面工程上证明了非共价氢键相互作用降低了接触电阻,展示了一种可扩展的解决方案,用于实现vdW触点以外的高性能和低功耗柔性电子产品。
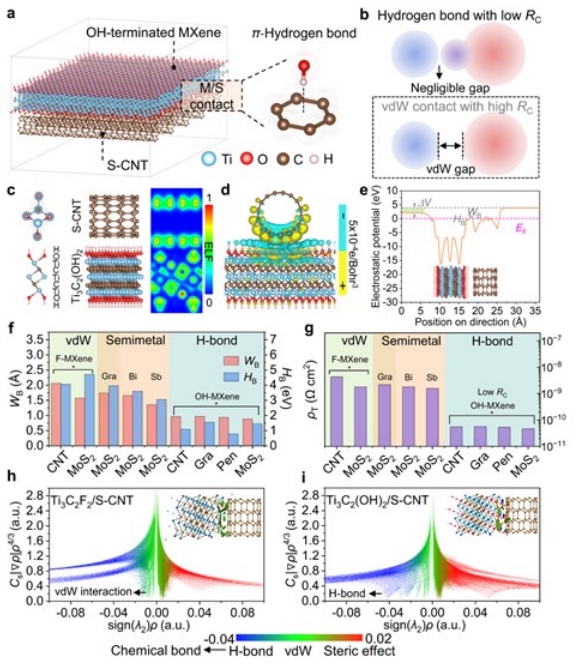
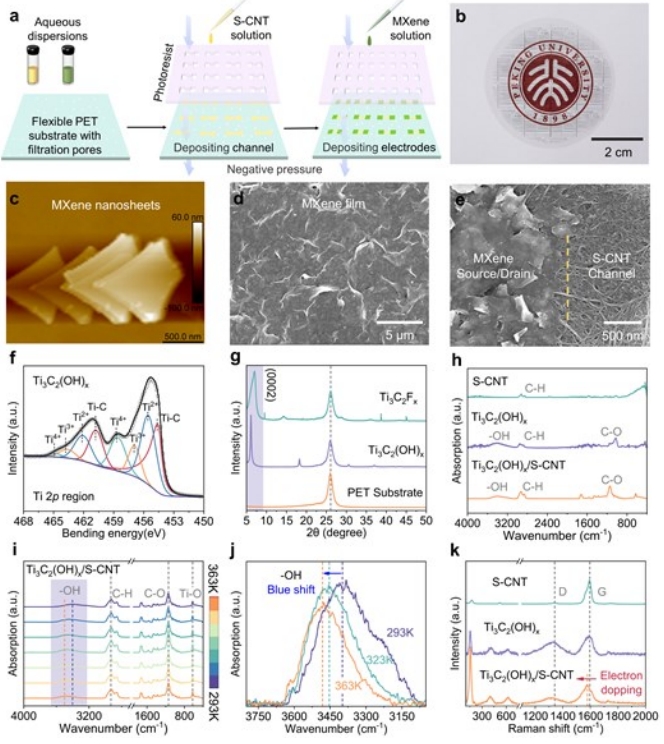
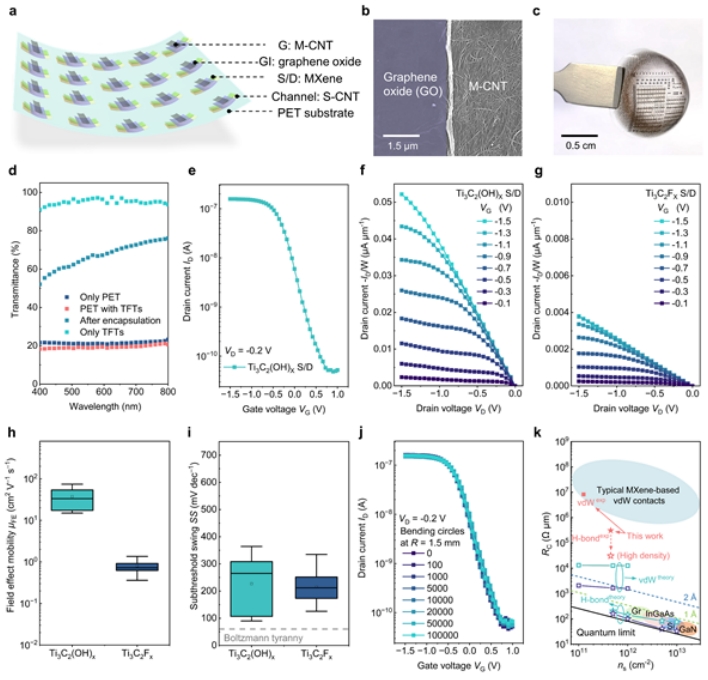
范德华(vdW)集成实现了低尺寸电子设备的清洁接触。然而,由于金属和半导体之间固有的vdW间隙,仍然存在额外的隧道接触电阻的限制。在这里,我们从理论计算中证明,更强的非共价氢键相互作用促进了电子隧穿,并显著降低了接触电阻,从而有望打破vdW接触的局限性。在表面工程MXene/碳纳米管金属/半导体异质结中实现了π-平面氢键接触,并观察到反常的温度相关隧穿电阻。通过氢键接触集成的低维柔性薄膜晶体管表现出优异的柔性和载流子迁移率,其数量级高于具有vdW接触的对应物。我们的战略展示了一种可扩展的解决方案,用于实现vdW触点以外的高性能和低功耗柔性电子产品。
Van der Waals (vdW) integration enables clean contacts for low-dimensional electronic devices. The limitation remains, however, that an additional tunneling contact resistance occurs, owing to the inherent vdW gap between the metal and the semiconductor. Here we demonstrate from theoretical calculations that stronger non-covalent hydrogen-bonding interactions facilitate electron tunneling and significantly reduce the contact resistance, thus promising to break the limitations of the vdW contact. π-Plane hydrogen-bonding contacts in surface-engineered MXene/carbon nanotube metal/semiconductor heterojunctions are realized, and an anomalous temperature-dependent tunneling resistance is observed. Low-dimensional flexible thin-film transistors integrated by hydrogen-bonding contacts exhibit both excellent flexibility and carrier mobility orders of magnitude higher than their counterparts with vdW contacts. Our strategy demonstrates a scalable solution for realizing high-performance and low-power flexible electronics beyond vdW contacts.
文章链接:
DFT计算中具有氢键和vdW接触的金属/半导体结的电学性能
金属/半导体异质结中氢键接触的实验证明
基于氢键的柔性薄膜晶体管的集成