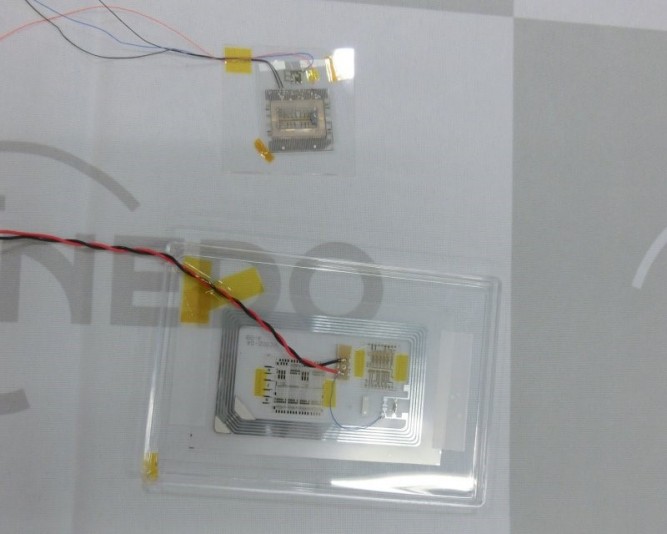
CMOS Circuit, Temperature Sensor Formed by Using Printing Technology
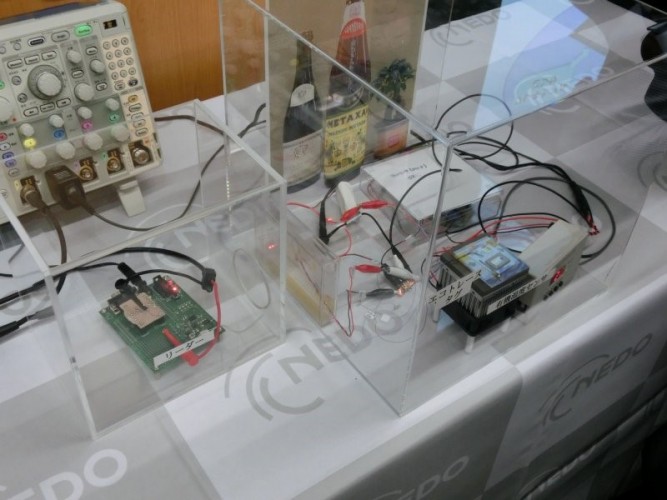
A Japanese research group formed a CMOS circuit and temperature sensor by using printing technology, connected them to an antenna for a frequency of 13.56MHz and transmitted temperature data.
The group, which consists of researchers from the University of Tokyo, Technology Research Institute of Osaka Prefecture, etc, made the announcement Jan 26, 2015.
The latest results were realized by using a single crystal organic semiconductor whose carrier mobility is 16.2cm2/Vs, which is more than 10 times higher than that of a conventional organic material. Because a vacuum process is not required, it is possible to reduce manufacturing cost by more than 90%, the group said.
To form the CMOS circuit, the "coating crystallization method," which was developed by the group, was used. With the method, a p- or n-type single crystal organic semiconductor material is mixed with a polymer with a high viscosity to make a mixed solution, which is, then, applied to a substrate.
When the solution is drying, polymer and single crystal organic material layers are formed on the lower and upper sides, respectively. P- and n-type lines are alternately drawn with a space in between, and electrodes are drawn on them and connected to form a semiconductor device.
As for digital circuits, the group formed a D-flip-flop circuit, which is required for memory, and a 4-bit shift register, which is necessary for data transmission.
The temperature sensor was realized by making use of the fact that the resistance value of the "PEDOT:PSS" organic polymer material changes depending on temperature. In addition, the group used an organic semiconductor material to form a circuit that converts analog resistance value data to digital data. Furthermore, the group made a rectifier circuit based on organic TFT elements made by using the coating crystallization method.
The research group made a high-performance organic TFT using a single crystal organic material in 2011, drove an LCD display using the coating crystallization method in 2012 and developed a low-cost RFID tag rectifier based on a single crystal TFT in 2014. And the group has already announced them. For the future, it plans to develop an RFID equipped with a temperature sensor for logistics management, aiming at commercialization.
Also, the group will conduct joint researches with companies that develop organic semiconductor materials, panel components, devices, etc, at "High-end Organic Semiconductor R&D/Education Center" for the development of organic electronics devices that operate at high speeds for a wide variety of applications.
The newly-developed system
An RFID and temperature sensor