Direct C-H Amination of Arenes with Alkyl Azides under Rhodium Catalysis
(June, 25th, reported by Dongqi Wang)
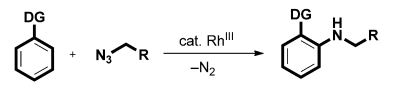
Ever since the seminal study by Curtius on the use of alkyl azides in organic chemistry, these readily available compounds have been widely used in C-N bond-forming reactions. Recently, Sukbok Chang and co-workers reported a straightforward procedure for the insertion of an amino group into arene C-H bonds by the use of alkyl azides as the nitrogen source. Both benzyl and aliphatic azides bearing a wide range of functional groups of high biological interest reacted readily with a range of substrates containing chelating groups under RhIII catalysis (Figure 1).
Figure 1a. A rhodium-catalyzed direct C-H amination with alkyl azides. DG=directing group
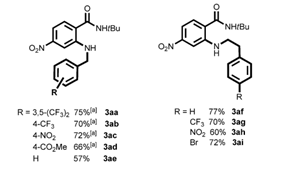
Figure 1b. Selected examples
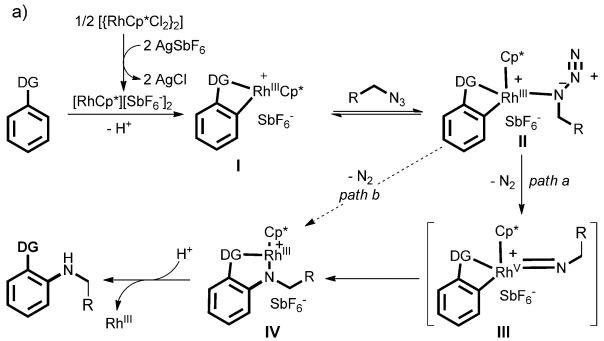
A plausible amination pathway is depicted in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Proposed mechanism of the direct C-H amination
The excellent functional-group tolerance observed will enable this transformation to be applied as a convenient route to synthetically and medicinally important amino compounds.