Monodisperse AgPd Alloy Nanoparticles and Their Superior Catalysis for the Dehydrogenation of Formic Acid
(Reported by Jolin)
Since fossil fuels are rapidly depleting and causing serious damage to the planet, hydrogen, which is renewable, environmentally friendly, becomes one of the most promising candidates to replace fossil fuels. Formic acid, the simplest carboxylic acid, has received considerable attention for it is suitable for easy transportation, refueling, and handling.
Recently, S. Sun et al. synthesized the monodisperse 2.2 nm AgPd nanoparticles, which were highly active heterogeneous catalysts for the dehydrogenation of FA. Alloy effects were fully studied through TEM, XRD and SPR and kinetic information were obtained by studying the concentration of the NPs catalyst, FA concentration, and the temperature effects. With the desired control on the NP sizes, compositons, and shapes, NP catalysis for the dehydrogenation of FA can be further optimized and a new type of heterogenerous catalyst may be developed for hydrogen generation and for hydrogen-based energy device applications.
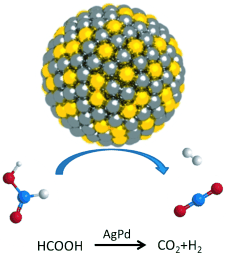
S. Sun et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, online.
