Publications
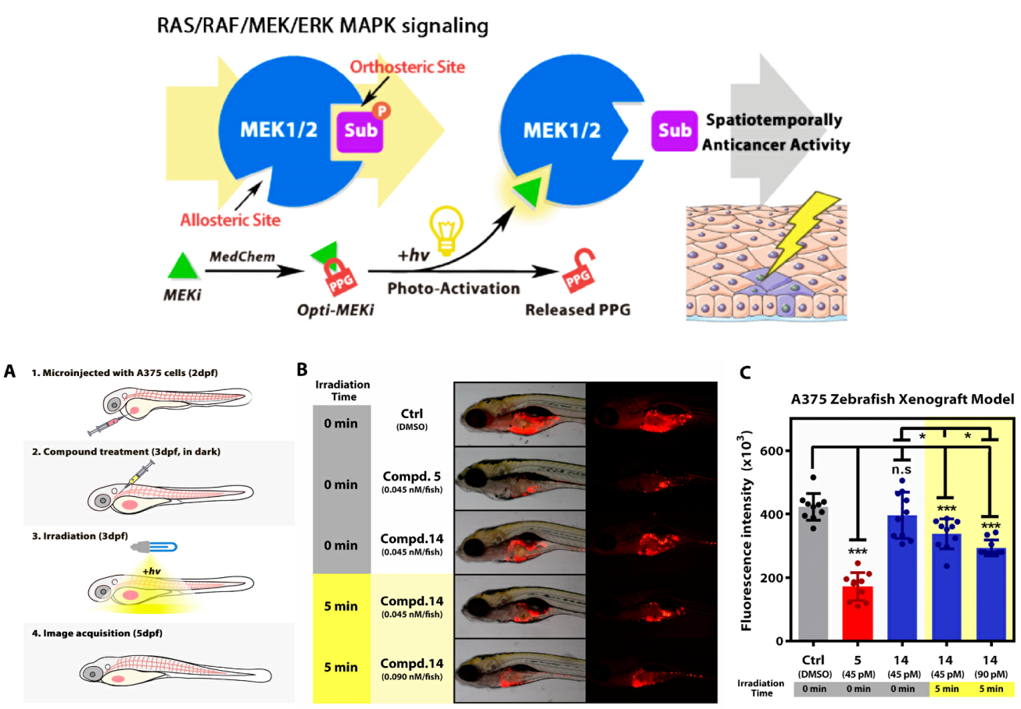
6. Chen, R.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Pan, Z., Discovery of novel photocaged ERK1/2 inhibitors as light-controlled anticancer agents. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58 (31), 4901-4904.
8. Wang, X.;

10. Xue, G.; Wang, K.; Zhou, D.; Zhong, H.*; Pan, Z.* “Light-Induced Protein Degradation with Photocaged PROTACs” J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 18370.

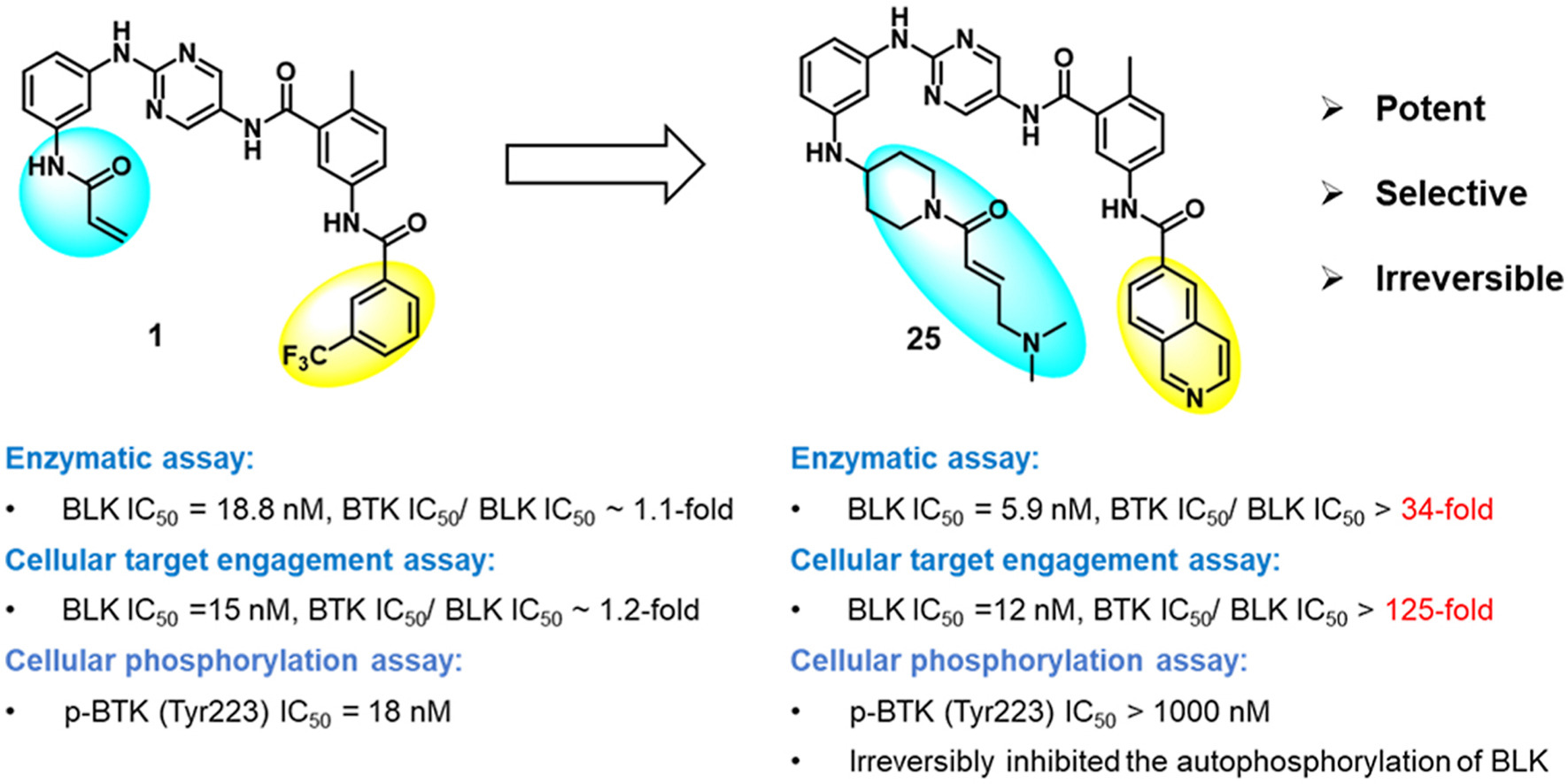
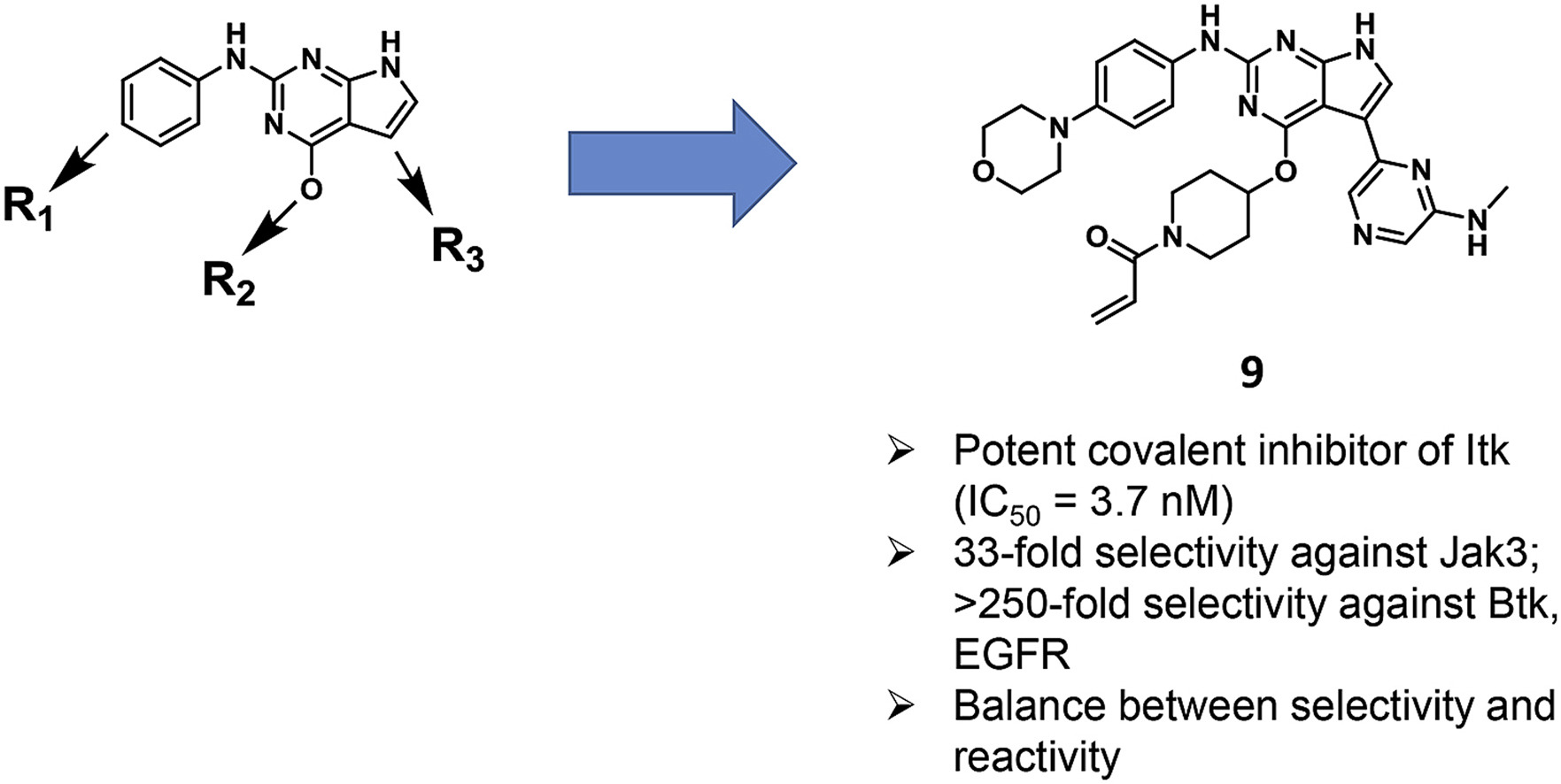
11. Tang, G.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Pan, Z.* “Discovery of 7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives as selective covalent irreversible inhibitors of interleukin-2-inducible T-cell kinase (Itk)” Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 173, 167.
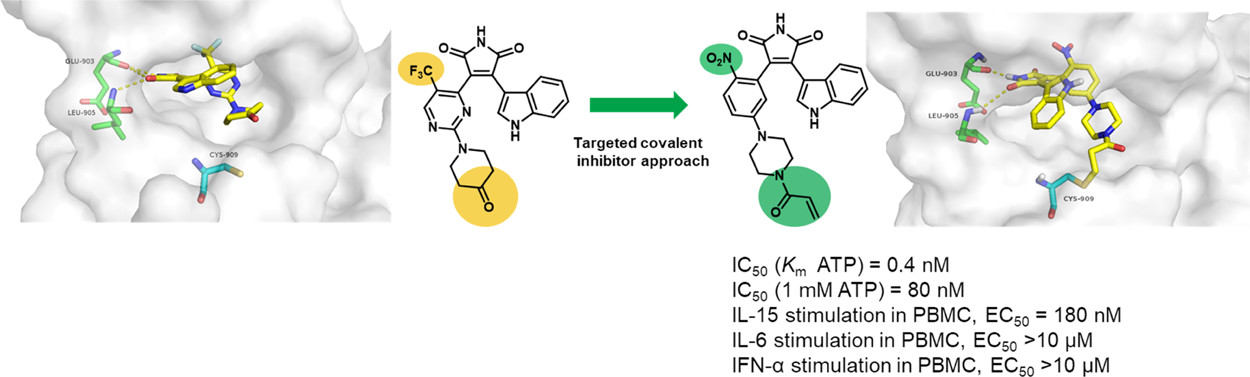
12. Shi, L.; Zhong, Z.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, Z.* “Discovery of an Orally Available Janus Kinase 3 Selective Covalent Inhibitor” J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 1054.
13. Yang, Z.; Liu, H.; Pan, B.; He, F.; Pan, Z.* “Design and synthesis of (aza)indolyl maleimide based covalent inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase 3β” Org. & Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 4127. 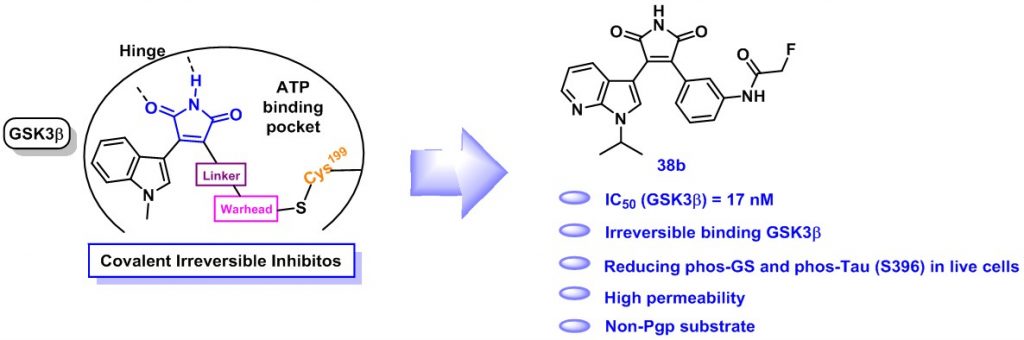
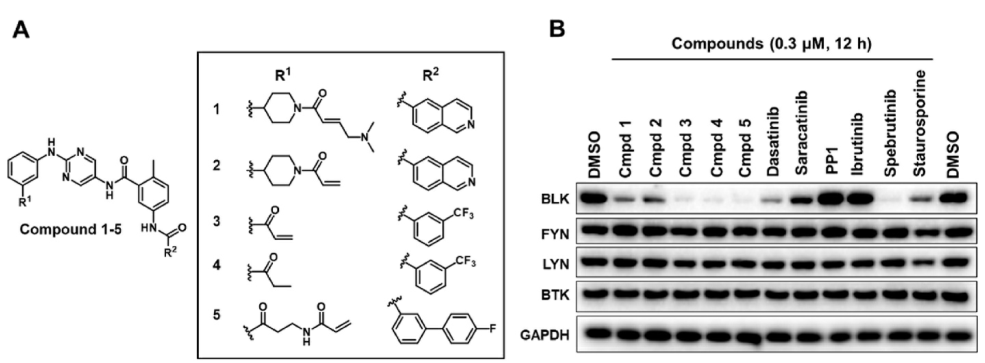
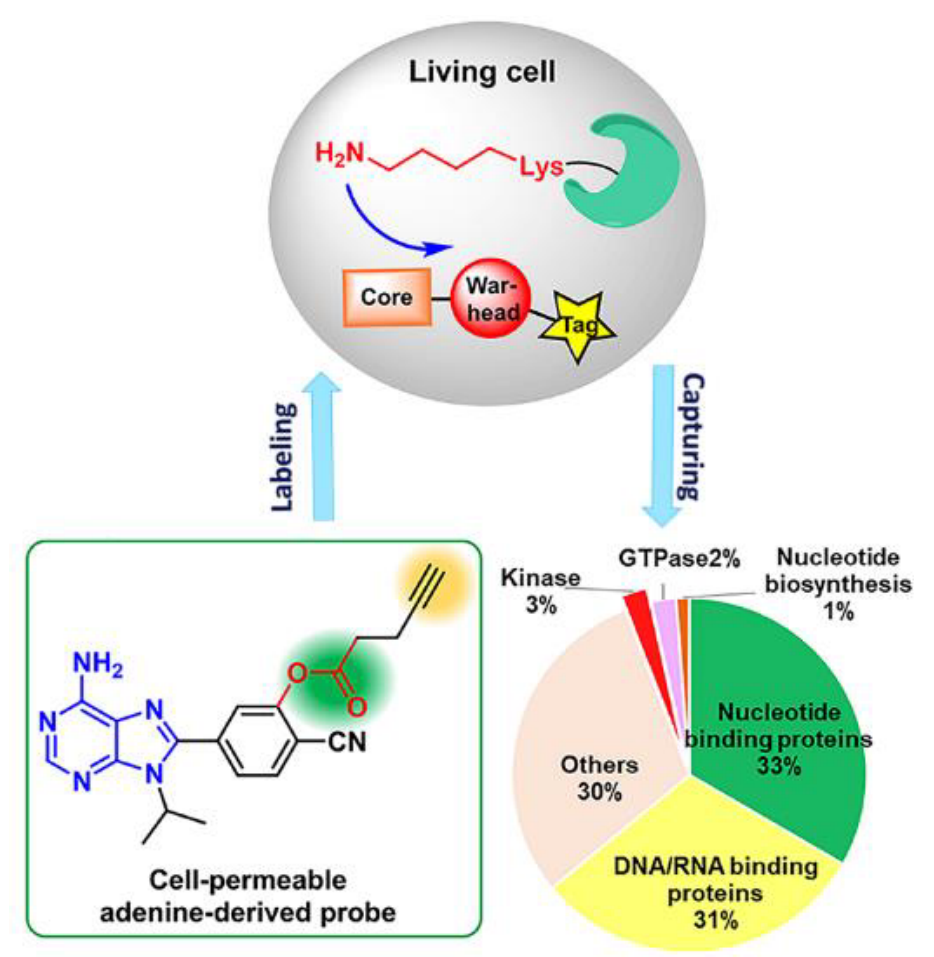
14. Chen, J.; Wang, X.; He, F.; Pan, Z.* “Development of a selective labelling probe for Bruton’s tyrosine kinase quantification in live cells” Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 1640. 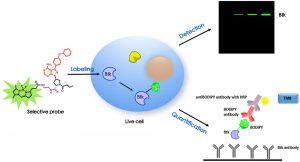
15. Wang, X.; Guo, T.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, Z.* “Covalent and selective immobilization of GST fusion proteins with fluorophosphonate-based probes” Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 4661 (Back Cover).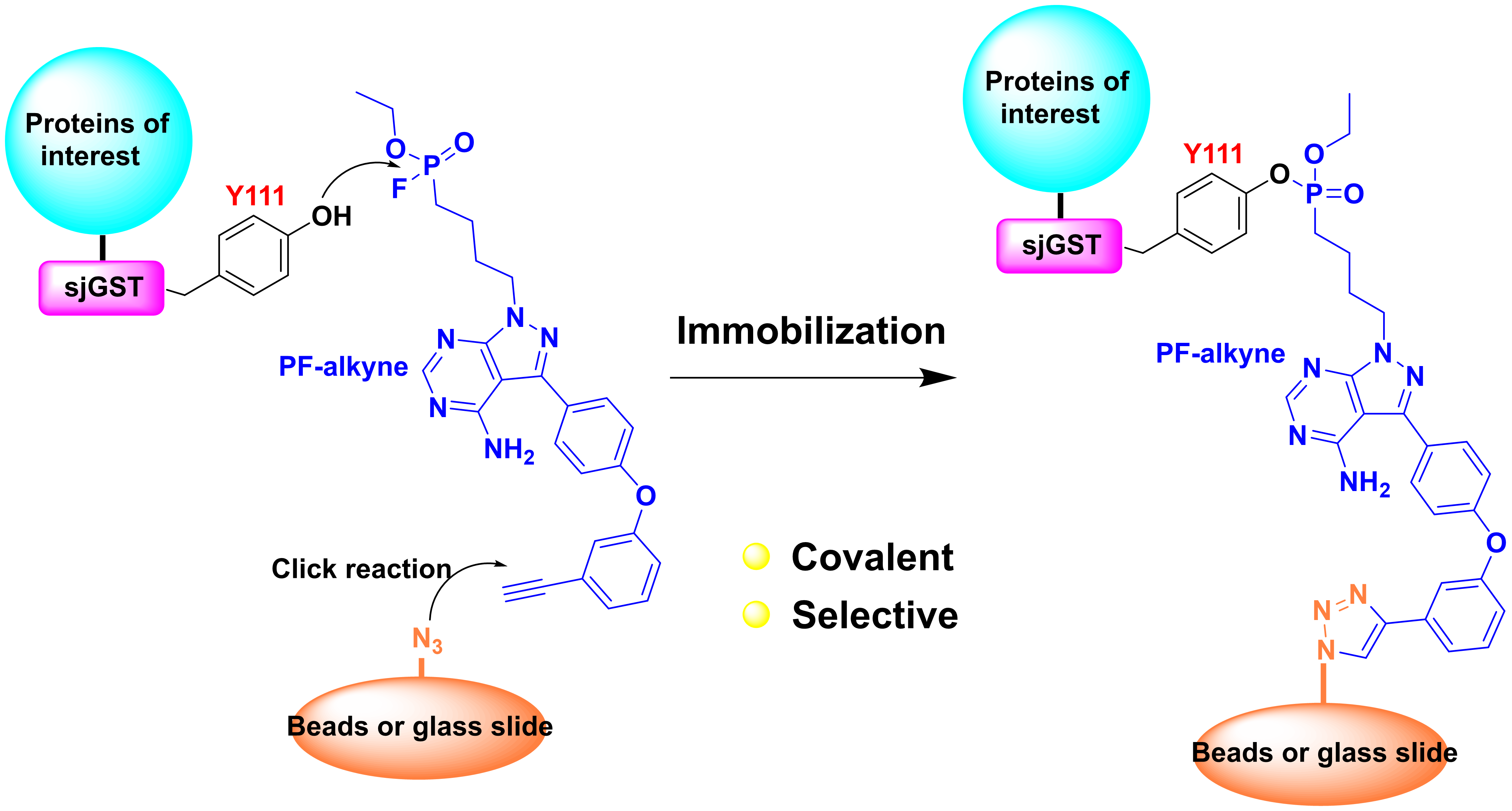

16. Zuo, Y.; Pan, Z*. “Small-molecule inhibitors of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase” Top. in Med. Chem. 2017. (Book Chapter)
17. Ping, L.; Ding, N.; Shi, Y.; Feng, L.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Shi, C.; Wang, X.; Pan, Z.*; Song, Y.*; Zhu, J.* “The Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib exerts immunomodulatory effects through regulation of tumor-infiltrating macrophages” Oncotarget 2017, 8, 39218.
18. Zuo, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, X.; Teng, Y.; Pan, Z.* “A novel 2,5-diaminopyrimidine-based affinity probe for Bruton’s tyrosine kinase” Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16136. 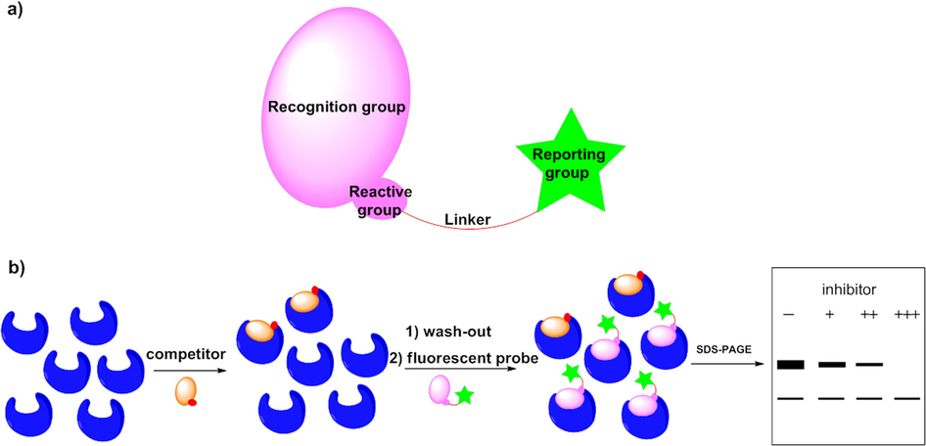
19. Ding, N.; Li, X.; Shi, Y.; Ping, L.; Wu, L.; Fu, K.; Feng, L.; Zheng, X.; Song; Y.*; Pan, Z.*; Zhu, J.* “Irreversible dual inhibitory mode: the novel Btk inhibitor PLS-123 demonstrates promising anti-tumor activity in human B-cell lymphoma” Oncotarget. 2015, 6, 15122.
20. Zhang, Q.; Liu, H.; Pan, Z.* “A general approach for the development of fluorogenic probes suitable for no-wash imaging of kinases in live cells” Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 15319. 
21. Liu, H.; Yang, Z.; Pan, Z.* “Synthesis of Highly Substituted Imidazolidine-2,4-dione (Hydantoin) through Tf2O-Mediated Dual Activation of Boc-Protected Dipeptidyl Compounds” Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 5902. ![]()
22. Zhou, Y.; Guo, T.; Tang, G.; Wu, H.; Wong, N-K.; Pan, Z.* “Site-selective Protein Immobilization by Covalent Modification of GST Fusion Proteins” Bioconjugate Chem. 2014, 25, 1911 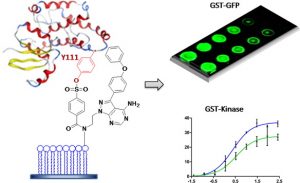
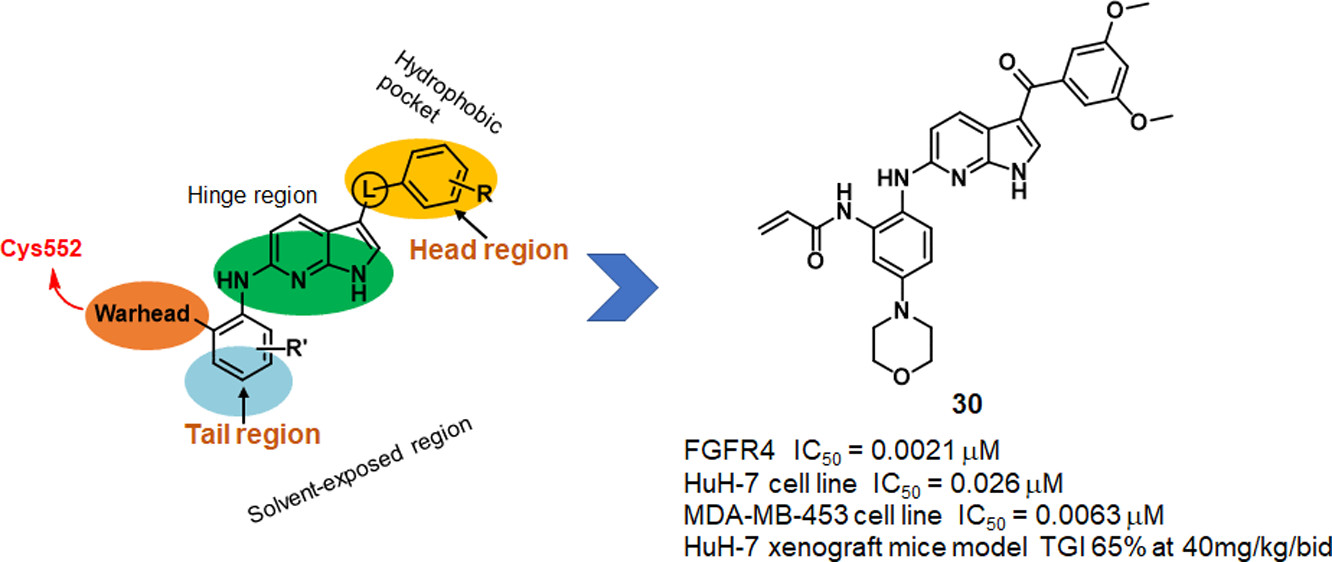
23. Li, X.; Zuo, Y.; Tang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, T.; Xia, M.; Ding, N.; Pan, Z.* “Discovery of a Series of 2,5-Diaminopyrimidine Covalent Irreversible Inhibitors of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase with in Vivo Antitumor Activity” J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 5112. 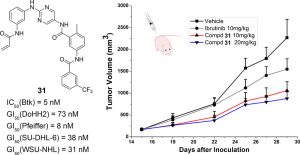
24. Zhou, Y.; Guo, T.; Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Galatsis, P.; Johnson, D.S.; Pan Z.* “Discovery of selective 2,4-diaminopyrimidinebased photoaffinity probes for glyoxalase I” Med. Chem. Commun. 2014, 5, 352. (Invited)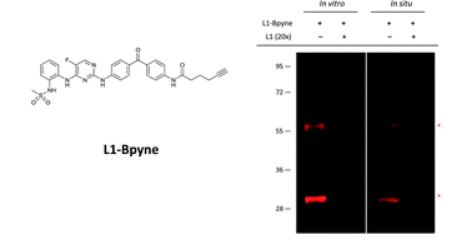
25. Zheng, J,; Lin, S.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, B.*; Yang, Z.*; Pan Z.* “Reductant-directed formation of PS-PAMAM-supported gold nanoparticles for use as highly active and recyclable catalysts for the aerobic oxidation of alcohols and the homocoupling of phenylboronic acids.” Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 6235. 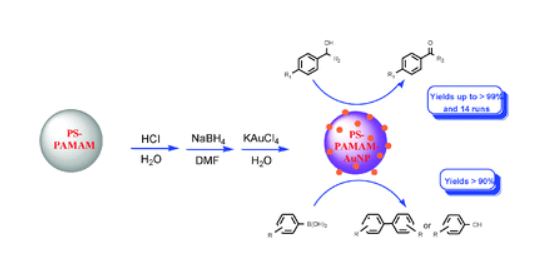
26. Honigberg, L.A.; Smith, A.M.; Sirisawad, M.; Verner, E.; Loury, D.; Chang, B.; Li, S.; Pan, Z.; Thamm, D.H.; Miller, R.A.; Buggy, J.J. “The Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor PCI-32765 Blocks B-cell Activation and Is Efficacious in Models of Autoimmune Disease and B-cell Malignancy” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13075.
Abstract: Activation of the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) signaling pathway contributes to the initiation and maintenance of B-cell malignancies and autoimmune diseases. The Bruton tyrosine kinase (Btk) is specifically required for BCR signaling as demonstrated by human and mouse mutations that disrupt Btk function and prevent B-cell maturation at steps that require a functional BCR pathway. Herein we describe a selective and irreversible Btk inhibitor, PCI-32765, that is currently under clinical development in patients with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. We have used this inhibitor to investigate the biologic effects of Btk inhibition on mature B-cell function and the progression of B cell-associated diseases in vivo. PCI-32765 blocked BCR signaling in human peripheral B cells at concentrations that did not affect T cell receptor signaling. In mice with collagen-induced arthritis, orally administered PCI-32765 reduced the level of circulating autoantibodies and completely suppressed disease. PCI-32765 also inhibited autoantibody production and the development of kidney disease in the MRL-Fas(lpr) lupus model. Occupancy of the Btk active site by PCI-32765 was monitored in vitro and in vivo using a fluorescent affinity probe for Btk. Active site occupancy of Btk was tightly correlated with the blockade of BCR signaling and in vivo efficacy. Finally, PCI-32765 induced objective clinical responses in dogs with spontaneous B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. These findings support Btk inhibition as a therapeutic approach for the treatment of human diseases associated with activation of the BCR pathway.
27. Zou, H.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Cui, Y.; Zhong, H.; Pan, Z.; Yang, Z.; Quan, J. “Benzo[e]isoindole-1,3-diones as Potential Inhibitors of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK-3). Synthesis, Kinase Inhibitory Activity, Zebrafish Phenotype, and Modeling of Binding Mode” J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 994. 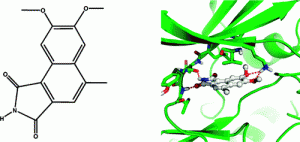
28. Pan, Z.* “Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase as a Drug Discovery Target” Drug News & Perspectives (Invited) Drug News & Perspectives 2008, 21, 357.
29. (伊布替尼—化合物的发现)Pan, Z.*; Scheerens, H.; Li, S.-J.; Schultz, B. E.; Sprengeler, P. A.; Burrill, L. C.; Mendonca, R. V.; Sweeney, M. D.; Scott, K. C. K.; Grothaus, P. G.; Jeffery, D. A.; Spoerke, J. M.; Honigberg, L. A.; Young, P. R.; Dalrymple, S. A. and Palmer, J. T. “Discovery of Selective Irreversible Inhibitors for Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase” ChemMedChem 2007, 2, 58.
Abstract: A series of highly selective irreversible inhibitors for Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) was developed using a structural bioinformatics approach. Their capabilities to modulate Btk's activity were characterized both in vitro and in vivo. Oral treatment with once‐a‐day dosing of compound 4 greatly inhibited disease development in a rodent rheumatoid arthritis (RA) model.
30. Pan, Z.*; Jeffery, D. A.; Chehade, K.; Beltman, J.; Clark, J. M.; Grothaus, P. G.; Bogyo, M.* and Baruch, A* “Development of Activity-based Probes for Trypsin-family Serine Proteases” Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 2882. 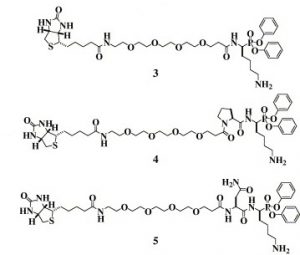
31. Hansen, K.K.; Sherman, P.M.; Cellars, L.; Andrade-Gordon, P.; Pan, Z.; Baruch, A.; Wallace, J.L.; Hollenberg, M.D. and Vergnolle, N. “A Major Role for Proteolytic Activity and Proteinase-activated Receptor-2 in the Pathogenesis of Infectious Colitis” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8363.
32. Trost, B.M.*; Pan, Z.; Zambrano, J. and Kujat, C. “Polymer-supported C2-Symmetric Ligands for Palladium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation Reactions” Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 4691. 
PATENTS