Biocompatible devices and Bioelectronics
With the gradual depletion of non-renewable resources and increasing awareness of environmental protection, the development of renewable and green resources has become a common goal worldwide. Some biomaterials, such as cellulose, chitin, DNA, and protein, originate from nature and pose no threat to the environment, making them particularly suitable for constructing green electronics. Biocompatible materials offer excellent biocompatibility and degradability, making devices prepared with these materials ideal for integrating bioelectronics and enabling direct use in wearable and implantable applications, such as biomedical detection and health monitoring.
Our group is dedicated to developing biocompatible electronic devices using various types of biomaterials, such as biocompatible neuromorphic devices, memristors, thin-film transistors, digital logic units, light-emitting devices, and sensors. Furthermore, we are exploring integration methods to realize multifunctional integration of bio-microelectronic device systems.
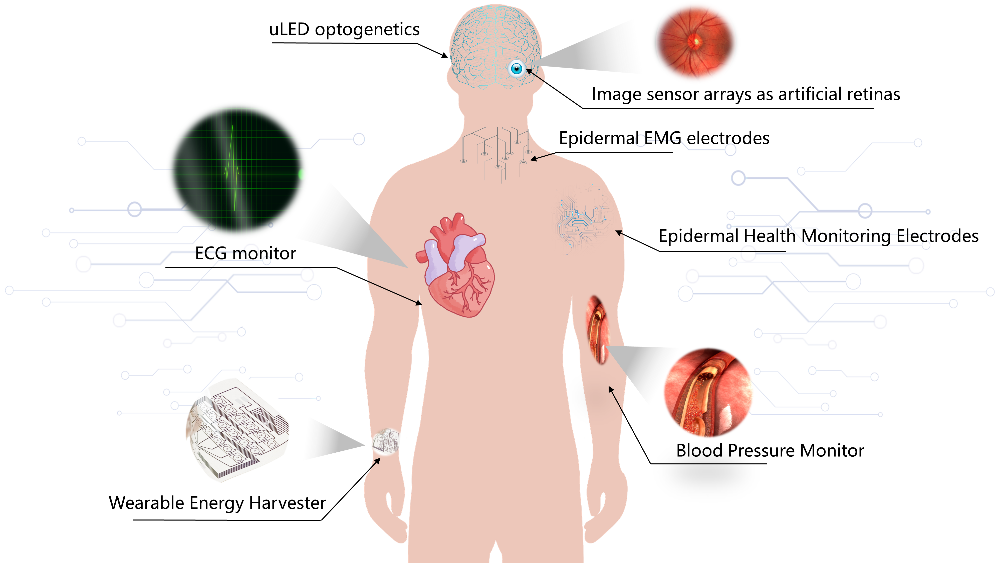
Figure 2-1 Bioelectronics has a wide range of promising applications in the field of implantable medicine.
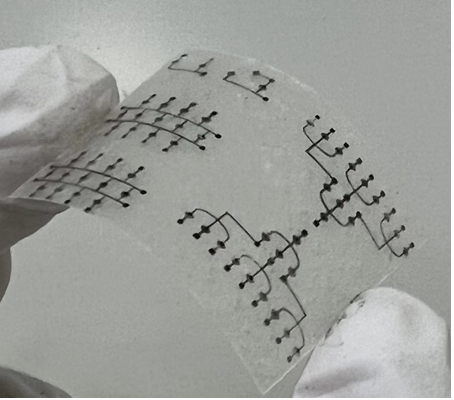

Figure 2-2 Biological tissue-based devices and circuits.
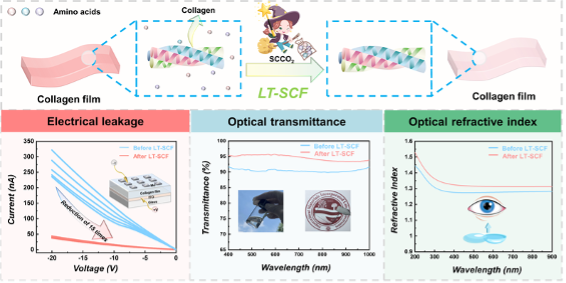
Figure 2-3 Optimization of the optic-electrical properties of collagen films.

