Emerging electronic devices
(1)RRAM
As information, the Internet of Things and cloud computing put higher requirements for semiconductor memories, the integration of circuits increases and the current mainstream memory—Flash—suffers from mutual crosstalk effects of adjacent memory cell and reliability issues during miniaturization. Among various emerging memories, resistive random-access memory (RRAM) is considered the most promising non-volatile memory in the next generation of memory devices due to its non-volatility, simple structure for three-dimensional integration, fast switching speed, low power consumption reliability and long-time retention characteristics.
Our research involves exploration of resistive switching materials, electrode and surrounding materials, optimization of device structure, and clarifying physicochemical mechanisms. We choose suitable CMOS-compatible materials to construct high-performance RRAMs and solve the uniformity and leakage problems in large-scale integration. The performance and reliability of the RRAM achieved by our group have reached the world's most advanced level. We are also deepening our cooperation with the industry to promote the progress and development of resistive memory in more fields.
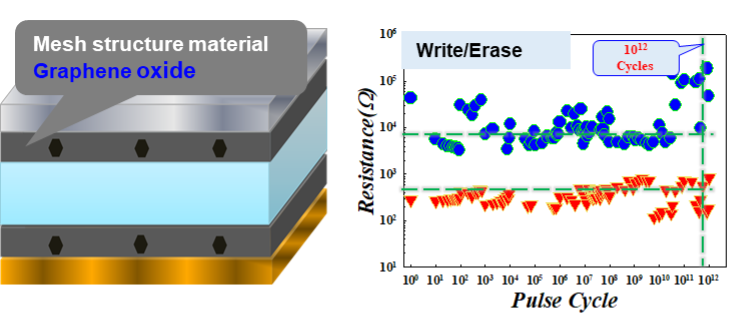
Figure 3-1 The double-layer doped resistive memory designed by our group, achieves ultra-high performance and reliability and reaches the world advanced level.
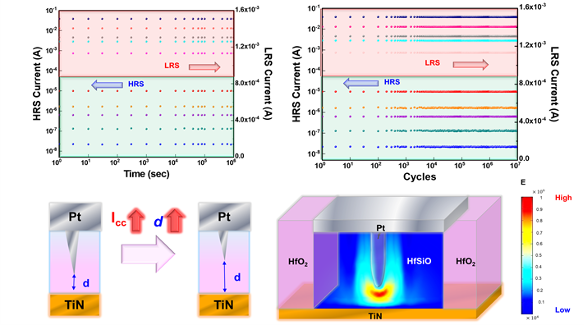
Figure 3-2 The effect of surrounding materials on the resistance performance.
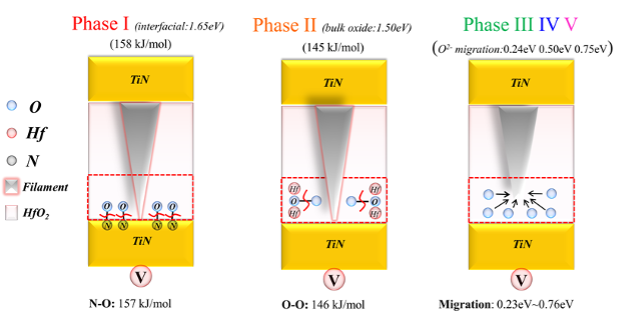
Figure 3-3 Clarifying the resistance mechanism through variable- temperature activation energy extraction method.
(2)Thin-film transistors
Nowadays, thin-film transistors (TFTs) are widely used in displays, such as large-screen TVs, smartphones, and tablet PCs. With the display technology develops toward higher resolution, larger size, higher frame rate, flexibility and transparency, improving the performance of TFTs is crucial. Our group is also dedicated to developing high-performance thin-film transistors, preparing flexible TFTs with excellent mechanical, electrical and optical properties through structural design and material selection; regulating their electrical, mechanical and optical properties, and investigating the underlying mechanisms.
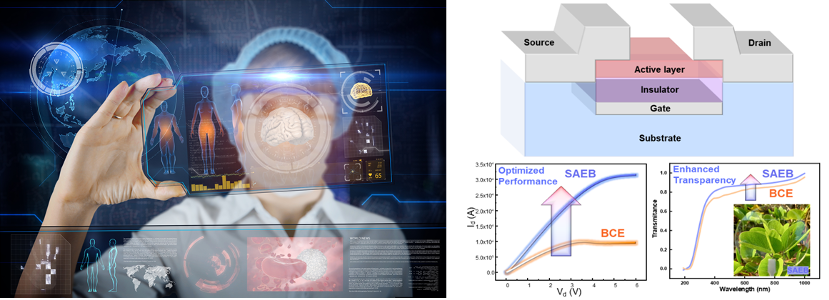
Figure 3-4 Embedded thin-film transistors with high performance and high transparency designed by Our group
(3)GaN-based Devices
Currently, the industry is undergoing a transformation toward the development of new energy and intelligent electronics, resulting in an increase in demand for power devices with higher efficiency, stability, and reliability, while also accounting for the cost of materials, environmental requirements, and application requirements. In order to achieve these requirements, third-generation wide-band semiconductor materials, such as GaN and SiC, which provide high temperature resistance, high power, and tolerance to severe environments, have become a focal point. Our research group investigates the structure, processing, physical and electrical characteristics of GaN- and SiC-based devices. In addition, we employ supercritical fluid techniques to further improve device performance and equip them with neuromorphic features in order to expand their application scenarios and circumstances.

Figure 3-5 The applications of GaN devices.

