Synthetic progress toward 11-epi-azadirachtin I
Azadirachtin A is a highly oxygenated tetranortriterpenoid isolated from the neem tree Azadirachta Indica A. Juss (Meliaceae). Azadirachtin A is a powerful insect repellent with low mammalian toxicity, however, there is limited structure-activity relationship information and it has an elusive mechanism-of-action.2 Various azadirachtin congeners possess remarkable antifeedant activity, such as azadirachtin I acts against Spodoptera litura with similar potency to azadirachtin A. The anti-insect properties of these azadirachtin-type limonoids are less well studied, partially due to limited availability.
Azadirachtin A possesses a number of intriguing structural elements, such as a highly oxygenated scaffold, sixteen contiguous chiral centers including seven quaternary ones, and a crowded C8–C14 bond. These fascinating and highly complex structural features have challenged as well as inspired synthetic chemists for decades, culminating in the “relay total synthesis” of azadirachtin A by Ley et al. One key to Ley’s success is the strategic disconnection of the C8–C14 bond, leading to the left- and right-wing (4–5) fragments.
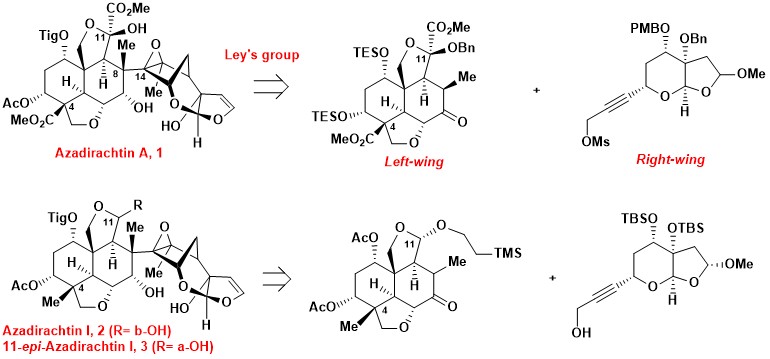
Synthetic progress toward 11-epi-azadirachtin I was reported as two related paper which were published on Org. Lett.. For more details, please see the paper online: https://web.pkusz.edu.cn/yang/93/ and https://web.pkusz.edu.cn/yang/92/.
