Publications
40.Synthetic Study toward the Total Synthesis of Maoecrystal V
J. X. Gong, G. Lin, C. C. Li* and Z. Yang*
A novel and concise approach for the construction of the core structure of maoecrystal V (1) has been developed. Utilizing the lead-mediated arylation of β-ketoesters and oxidative dearomatization/IMDA reaction as key steps, the two consecutive all-carbon quaternary centers (C-9 and C-10) were constructed in a stereoselective manner. The developed chemistry paves the way for the total synthesis of this fascinating natural product.

39. Unexpected Regioselectivity in the Synthesis of Pyranonaphthoquinone via the Diels−Alder Reaction
Y. Cui, H. Jiang, Z. T. Li, N. Wu, Z. Yang* and J. M. Quan*
The unusual regioselectivity in the Diels−Alder reactions of pyranoquinone 1 with (4,4-dimethoxybuta-1,3-dien-2-yloxy)trimethylsilane 2 are explored by both computations and experiments. The regioselectivity is controlled by the electrostatic interaction of the lactone ring-oxygen and the vicinal quinone oxygen on the transition structure, which can be tuned by the terminal methyl group of the butadienes.

38.Formal Total Synthesis of N-Methylmaysenine
L. Wang, J. X. Gong, L. J. Deng, Z. Xiang, Z. X. Chen, Y. Wang, J. H. Chen*, Z. Yang*
A novel synthetic approach for the formal total synthesis of N-methylmaysenine (1) has been developed. Key steps involve the Ti-mediated vinylogous Mukaiyama aldol reaction of chiral ketene silyl N,O-acetal with β-dithiane-substituted aldehyde, an aldol condensation, and a ring-closing metathesis reaction.

37.Characterization and Development of Novel Small-Molecules Inhibiting GSK3 and Activating Wnt Signalling
H. B. Zhong, H. X. Zou, M. V. Semenov, D. Moshinsky, X. He, H. Huang, S. Li, J. M. Quan, Z. Yang, S. Lin*
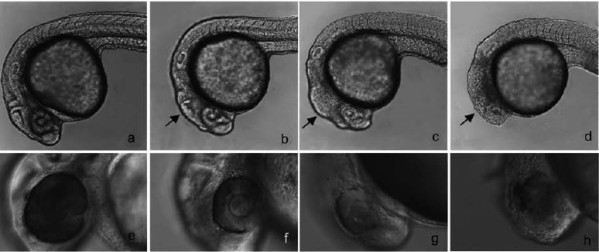
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) is an essential component of the Wnt signaling pathway and plays important roles in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. As GSK3 is abnormally upregulated in several diseases including type II diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease and cancer, it has been regarded as a potential drug target. During zebrafish development, inhibition of GSK3 leads to ectopic activation of the Wnt pathway, resulting in a headless embryo. Using this phenotype as an assay we screened a chemical library of 4000 compounds and identified one novel compound, 3F8, which specifically inhibits eye and forebrain formation in zebrafish embryos, resembling a typical Wnt overexpression phenotype. Cell reporterassays, chemical informatics analysis and in vitrokinase experiments revealed that 3F8 is a selective GSK3 inhibitor, which is more potent than SB216763, a commonly used GSK3inhibitor. Based on the structure of 3F8, a new generation of compounds inhibiting GSK3 was synthesized and validated by biological assays. Together, 3F8 and its derivatives could be useful as new reagents and potential therapeutic candidates for GSK3 related diseases.
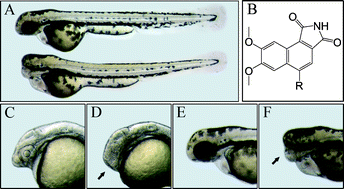
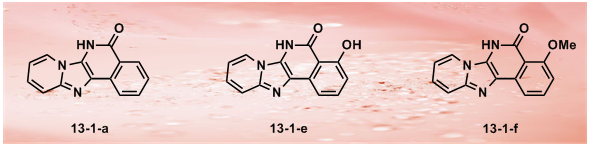
36.Identifying Tumor Cell Growth Inhibitors by Combinatorial Chemistry and Zebrafish Assays
J. Xiang, H. B. Yang, C, Che, H. X. Zou, H. B. Yang, Y. Wei, J. M. H. Zhang*, Z. Yang, S. Lin*
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) play important roles in regulating cell cycle progression, and altered cell cycles resulting from over-expression or abnormal activation of CDKs observed in many human cancers. As a result, CDKs have become extensive studied targets for developing chemical inhibitors for cancer therapies; however, protein kinases share a highly conserved ATP binding pocket at which most chemical inhibitors bind, therefore, a major challenge in developing kinase inhibitors is achieving target selectivity. To identify cell growth inhibitors with potential applications in cancer therapy, we used an integrated approach that combines one-pot chemical synthesis in a combinatorial manner to generate diversified small molecules with new chemical scaffolds coupled with growth inhibition assay using developing zebrafish embryos. We report the successful identification of a novel lead compound that displays selective inhibitory effects on CDK2 activity, cancer cell proliferation, and tumor progression in vivo. Our approaches should have general applications in developing cell proliferation inhibitors using an efficient combinatorial chemical genetic method and integrated biological assays. The novel cell growth inhibitor we identified should have potential as a cancer therapeutic agent.