Publications
155.Stereoselective Synthesis of trans-Decalin-Based Spirocarbocycles via Photocyclization of 1,2-Diketones
Sijia Chen, Zhongchao Zhang, Chongguo Jiang, Chunbo Zhao, Haojie Luo, Jun Huang*, and Zhen Yang*
ACS Omega 2021, 6(29), 18848–18859
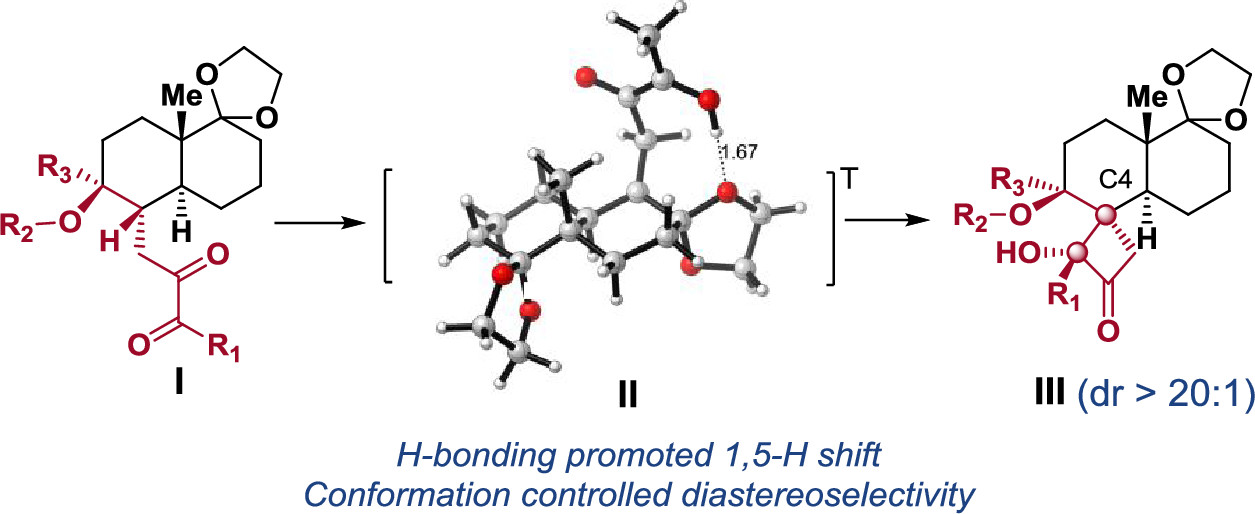
Diastereoselective synthesis of the trans-decalin-based α-hydroxyl butanone spirocarbocycles bearing all-carbon quaternary stereogenic centers has been achieved via Norrish–Yang photocyclization of trans-decalin-substituted-2,3-butanediones using daylight. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations suggest that this diastereoselective reaction is affected by both substrate conformation and intramolecular hydrogen bonds. The developed chemistry could be applied to synthesizing the derivatives of the trans-decalin-based biologically important natural products.
154.Synthesis of Desacyl Furanmonogones A and B
Dian Li, Jinfeng Yang, Bingyan Liu, Jianxian Gong,* and Zhen Yang*
Org. Lett. 2021, 23(12), 4532–4537
A strategy for the stereoselective synthesis of desacyl furanmonogones A and B has been achieved. The key steps in this synthesis are (1) an Fe(ClO4)3-mediated oxidative radical cyclization for construction of a cis-fused [5–6]-bicyclic core with a bridged lactone substitute, (2) a phosphorane-mediated rearrangement to convert the cis-fused [5–6]-bicyclic core to the corresponding trans-fused [5–6]-bicyclic core, and (3) a Au-catalyzed cascade reaction for formation of the 4,5-seco-3(2H)-furanone motif.
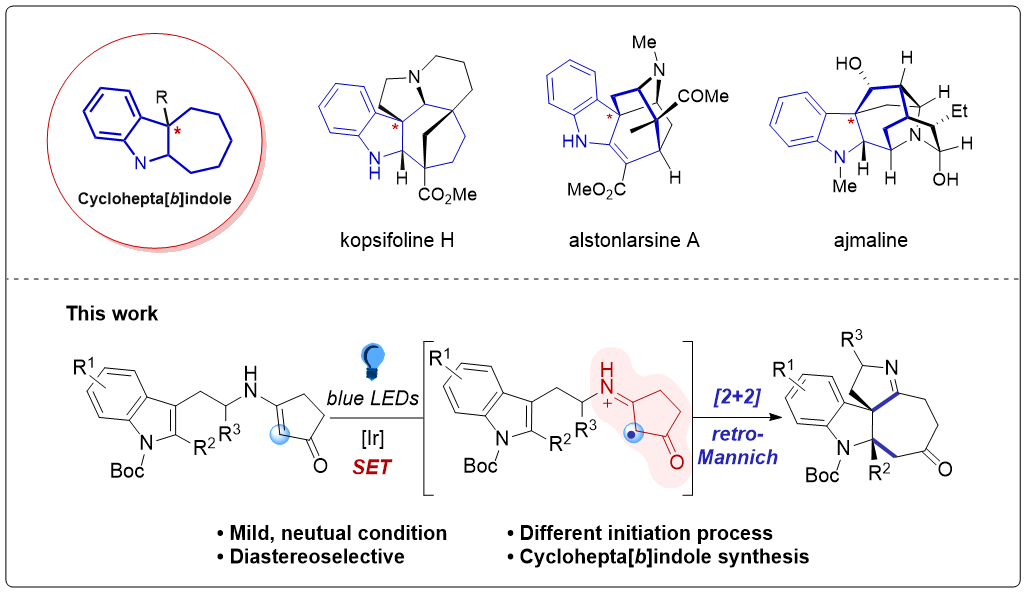
153.Stereoselective Synthesis of Cyclohepta[b]indoles via Visible‐Light‐Induced [2+2]‐Cycloaddition/retro‐Mannich‐type Reactions
152.Navigating the Pauson–Khand Reaction in Total Syntheses of Complex Natural Products
Zhen Yang*
Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54(3), 556–568
“Total synthesis endeavors provide wonderful opportunities to discover and invent new synthetic reactions as a means to advance organic synthesis in general. Such discoveries and inventions can occur when the practitioner faces intransigent problems that cannot be solved by known methods and/or when method improvements are desired in terms of elegance, efficiency, cost-effectiveness, practicality, or environmental friendliness” (K. C. Nicolaou et al. from their review in CCS Chem.2019, 1, 3–37). To date tens of thousands of bioactive compounds have been isolated from plants, microbes, marine invertebrates, and other sources. These chemical structures have been studied by chemists who scanned the breadth of natural diversity toward drug discovery efforts. Drug-likeness of natural products often possesses common features including molecular complexity, protein-binding ability, structural rigidity, and three-dimensionality. Considering certain biologically important natural products are scarce from natural supply, total synthesis may provide an alternative solution to generating these compounds and their derivatives for the purpose of probing their biological functions. Natural products bearing quaternary carbon stereocenters represent a group of biologically important natural entities that are lead compounds in the development of pharmacological agents and biological probes. However, the stereocontrolled introduction of quaternary carbons, with vicinal patterns that substantially expand the complexity of molecular architectures and chemical space in particular, presents distinct challenges because of the high steric repulsion between substituents. Though remarkable advance has been seen for quaternary carbon stereocenter generation, the process remains a daunting challenge given that the formation of highly congested stereocenters increases the difficulty in achieving orbital overlap.
In the past two decades, our group has initiated a program to develop synthetic strategies and methods with the aim of advancing the frontiers of the total syntheses of biologically important complex natural products bearing all-carbon quaternary stereogenic centers. Typical endeavors have involved the use of a Pauson–Khand (PK) reaction as a key step in constructing core structures with all-carbon quaternary stereogenic center(s), with the aid of well-orchestrated thiourea–Co- and thiourea–Pd-catalyzed PK reactions. These methodological advances have enabled us to achieve total syntheses of a series of topologically complex natural products with diverse structural features. These methods will enable the assembly of molecules with improved biological functions and provide tool compounds for elucidation of mechanism of action or identification of potential cellular targets.
151.Asymmetric Total Synthesis of (−)-Spirochensilide A, Part 2: The Final Phase and Completion
Xin-Ting Liang, Bao-Chuan Sun, Nan Zhang, Zhong-Chao Zhang, Yuan-He Li, Qian-Qian Xu, Chang Liu, Jia-Hua Chen,* and Zhen Yang*
J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86(3), 2158–2172
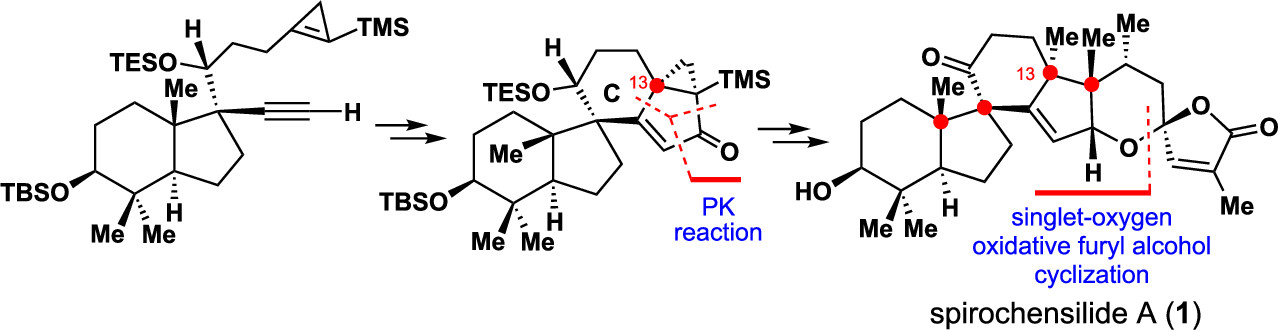
The final phase of the total synthesis of (−)-spirochensilide A is described. A tungsten-mediated cyclopropene-based Pauson–Khand reaction was developed to form the spiral CD ring system with desired stereochemistry at the C13 quaternary center. Other important steps enabling completion of this synthesis included an intermolecular aldol condensation to link the ABCD core with the EF fragment and a Cu-mediated 1,4-addition to stereoselectively install the C21 stereogenic center. The chemistry developed for this total synthesis of (−)-spirochensilide A (1) will aid the synthesis of polycyclic natural products bearing this unique spiral ring system.